Effective meetings are crucial for achieving goals and driving progress. A well-structured agenda is the cornerstone of any successful meeting. This guide demonstrates how to create a clear and focused meeting agenda using the powerful visual tool of a mind map. By following these steps, you can ensure your meetings are productive and efficient, leading to tangible results.
This comprehensive guide will walk you through the process of developing a meeting agenda from initial planning to final execution. Learn how to translate your ideas into a structured format that keeps the meeting on track and maximizes participation. The visual nature of mind maps will enable you to easily brainstorm, organize, and prioritize tasks for a more productive meeting experience.
Defining the Purpose of a Meeting Agenda

A meeting agenda serves as a roadmap for productive discussions and decisions. It Artikels the topics to be addressed, ensuring that the meeting stays focused and achieves its intended objectives. A well-structured agenda is crucial for effective meetings, preventing wasted time and ensuring that all important points are covered.A clear agenda provides a framework for the meeting, allowing participants to prepare adequately and contribute meaningfully.
It also serves as a record of the decisions made and actions assigned, facilitating accountability and follow-up. This structure, in turn, enhances the efficiency and overall effectiveness of the meeting.
Defining a Meeting Agenda
A meeting agenda is a structured Artikel of the topics and items to be discussed in a meeting. It acts as a guide, ensuring the meeting stays focused and achieves its objectives. A well-defined agenda minimizes unproductive discussions and maximizes the value of the meeting time. It serves as a shared understanding of the meeting’s purpose for all participants.
Importance of a Clear Agenda
A clear agenda is essential for effective meetings. It guides the discussion, ensuring that all important points are addressed and that the meeting stays on track. This structured approach helps participants prepare adequately and contributes to a more productive and focused meeting. A clear agenda also facilitates decision-making, ensuring clarity and accountability.
Objectives of a Meeting Agenda
A meeting agenda can serve various objectives, depending on the type of meeting. It can establish the purpose of the meeting, Artikel the discussion points, allocate time for each item, and facilitate decision-making. It can also help ensure that all relevant parties are informed and prepared for the meeting. By clearly defining objectives, a meeting agenda contributes to a more focused and efficient meeting.
Best Practices for Determining Meeting Purpose
Determining the purpose of a meeting is crucial for creating a relevant agenda. Before drafting the agenda, consider the meeting’s goals and desired outcomes. Who are the participants, and what are their specific roles and responsibilities? What decisions need to be made? Clearly defining the meeting’s objective is the first step towards a productive agenda.
This step will determine the scope and focus of the agenda. Understanding the meeting’s objective will also help in deciding the meeting’s duration and the appropriate participants.
Comparing Agendas for Different Meeting Types
| Meeting Type | Key Purpose | Typical Agenda Items | Time Allocation Considerations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Project Updates | Review progress, identify roadblocks, and plan next steps. | Project milestones, tasks completed, outstanding issues, action items, next steps. | Allocate time for each project component, ensuring adequate time for discussion and problem-solving. |
| Brainstorming Sessions | Generate creative ideas and solutions. | Problem statement, brainstorming techniques, idea generation, categorization of ideas, action items. | Allow ample time for free-flowing discussion and idea sharing. |
| Problem-Solving Sessions | Identify and address a specific problem. | Problem definition, analysis of the problem, identification of potential solutions, evaluation of solutions, decision-making. | Allocate time for thorough analysis and discussion, leading to well-reasoned solutions. |
This table provides a comparison of meeting agendas across different meeting types. Each meeting type has distinct objectives and requires an agenda that aligns with these objectives. Careful consideration of the meeting’s purpose is vital for a successful outcome.
Utilizing Mind Maps for Agenda Generation
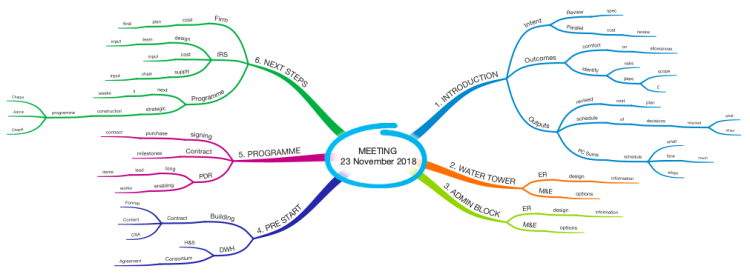
A well-structured meeting agenda is crucial for effective collaboration and achieving desired outcomes. Mind maps offer a powerful visual tool for generating these agendas, facilitating brainstorming and ensuring all critical points are addressed. This approach transforms a potentially disorganized list of items into a clear, hierarchical framework.Mind maps leverage the human brain’s natural associative thinking patterns. By visually connecting related ideas, they enable a more comprehensive and insightful approach to agenda creation.
This visual structure fosters a more dynamic and engaging brainstorming session, enabling participants to contribute ideas effortlessly and identify connections between seemingly disparate topics.
Visual Structure and Brainstorming
Mind maps capitalize on the visual nature of human understanding. Their branching structure mirrors the way our minds connect ideas. The central idea, clearly defined, acts as the focal point for the entire meeting’s purpose. Branches emanating from this central idea represent major discussion points. Sub-branches then illustrate supporting details and specific tasks or questions.
This visual organization significantly enhances brainstorming by encouraging the exploration of multiple avenues of thought, thus fostering a richer and more complete agenda.
Key Elements of a Mind Map
The core of a mind map lies in its hierarchical structure. A central idea, representing the meeting’s objective, is placed at the center. From this core, branches extend, representing major topics related to the meeting’s goal. Sub-branches, further branching out, delineate specific items for discussion. This branching structure allows for a detailed breakdown of the agenda, ensuring no crucial element is overlooked.
By breaking down complex topics into smaller, more manageable components, a mind map creates a clear roadmap for the meeting.
Translating a Mind Map to a Structured Agenda
Converting a mind map into a formal agenda involves systematically transferring the visual representation into a written format. The central idea becomes the meeting title. Major branches translate into agenda items, and sub-branches become supporting points within each item. This conversion ensures a smooth transition from a creative brainstorming session to a well-organized meeting. The structured agenda, derived from the mind map, ensures a focused and productive meeting.
Examples of Mind Map Structures for Different Meeting Types
The structure of a mind map can be tailored to the specific nature of the meeting. For a project review, the mind map might focus on project milestones, tasks, and outcomes. For a problem-solving session, the map could center on the problem, potential causes, and proposed solutions. An effective mind map adapts to the meeting’s purpose, creating a clear and effective agenda.
Mind Map Structure for a Problem-Solving Meeting
A problem-solving meeting requires a structured approach to identify the root cause and develop solutions. A simple mind map structure could be as follows:
| Central Idea | Branch 1: Problem Definition | Branch 2: Root Cause Analysis | Branch 3: Proposed Solutions |
|---|---|---|---|
| Problem Solving Meeting |
|
|
|
This structure ensures a systematic approach to problem-solving, enabling the team to comprehensively address the issue at hand. The structured format allows for a thorough examination of the problem and the development of effective solutions.
Structuring the Meeting Agenda with Mind Map Components
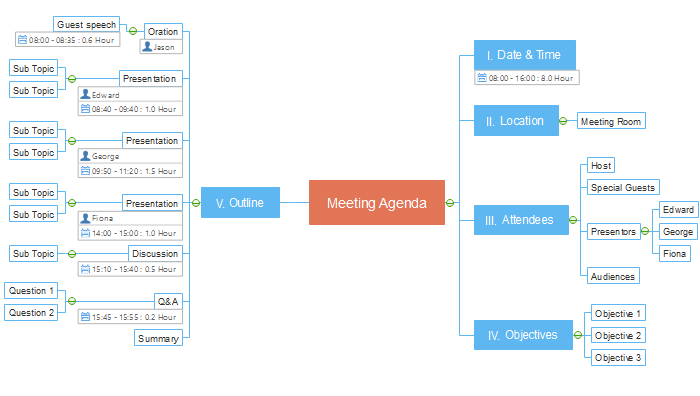
A well-structured meeting agenda, derived from a mind map, is crucial for efficient use of time and productive outcomes. A clear and concise agenda ensures that all key topics are addressed and that the meeting stays on track. This section details the steps to effectively create a meeting agenda using a mind map, emphasizing the importance of time allocation and breakdown of complex subjects.Effective meeting agendas are not just lists of topics; they are carefully crafted roadmaps that guide the discussion.
This approach enables participants to focus on the intended objectives and contribute meaningfully to the discussion.
Steps in Creating a Meeting Agenda Using a Mind Map
Creating a meeting agenda using a mind map involves several key steps. First, meticulously expand on the central theme, identifying key topics and s. Second, allocate appropriate time slots for each item. Finally, meticulously organize the agenda into a structured format, ensuring clarity and facilitating smooth progress.
- Brainstorming and Topic Identification: Begin by expanding the central theme, which is the meeting’s objective. This process helps to identify all the major topics and s related to the central theme. Thorough brainstorming ensures that no relevant area is overlooked. This is vital for comprehensive coverage and prevents crucial points from being omitted.
- Time Allocation: Assigning time slots to each agenda item is critical. This helps maintain a structured flow and ensures that sufficient time is allocated to each topic. Realistic time estimations for each item are essential, considering the complexity of the subject matter and the anticipated discussion. Avoid overestimating or underestimating the time required.
- Agenda Item Refinement: If a topic appears complex, break it down into smaller, more manageable agenda items. This process enhances the meeting’s clarity and keeps the discussion focused on specific points. Clearly defining smaller agenda items leads to a more productive and efficient meeting.
- Agenda Item Prioritization: Consider the relative importance of each agenda item. This helps in organizing the agenda in a logical order, ensuring that crucial issues are addressed first. Prioritizing items according to their importance or urgency helps the meeting proceed in a meaningful and productive direction.
Key Topics to Include in the Agenda
The meeting agenda should contain essential topics related to the meeting’s purpose. This ensures that the meeting remains focused on the intended goals and avoids unnecessary tangents. Key topics typically include the meeting’s objectives, proposed actions, and potential decision points.
- Meeting Objectives: The meeting’s primary purpose or goal should be clearly stated. This establishes the direction for the discussion.
- Action Items: Any actions required after the meeting should be explicitly noted. This includes assigning responsibilities and deadlines to ensure that follow-up tasks are completed.
- Potential Decisions: The agenda should highlight topics where decisions might be made. This helps in planning the necessary discussions and voting processes, if applicable.
- Discussion Points: Key issues or topics that need discussion should be included. These are specific aspects that require detailed discussion and deliberation.
Importance of Assigning Time Slots
Assigning time slots to different agenda items is vital for managing the meeting’s flow. This structured approach helps to maintain a productive pace and prevent the meeting from exceeding its allocated time. It creates a clear schedule and ensures all essential topics receive appropriate attention.
- Maintaining Pace: Time slots ensure the meeting doesn’t drag on unnecessarily. This allows for sufficient time for each topic without rushing through key discussions.
- Prioritization: Time allocation implicitly prioritizes certain agenda items. This allows for a more focused discussion on critical topics.
- Meeting Efficiency: Time slots enhance meeting efficiency by keeping the discussion focused and on schedule. This is crucial for effective use of time and minimizing unnecessary delays.
Breaking Down Complex Topics
Breaking down complex topics into smaller, more manageable items ensures clarity and focus. This method promotes a more productive discussion, as participants can concentrate on specific aspects of the subject. It also enhances understanding and facilitates consensus building.
- Example: Instead of “Develop Marketing Strategy,” break it down into “Define Target Audience,” “Develop Messaging,” “Artikel Marketing Channels,” and “Set Budget.” This approach allows for a more thorough and detailed discussion of each component.
Format for Structuring a Meeting Agenda
The following table Artikels a format for structuring a meeting agenda based on a mind map.
| Agenda Item | Description | Estimated Time (minutes) | Assigned To |
|---|---|---|---|
| Define Project Scope | Clarify project boundaries and deliverables | 15 | Project Manager |
| Review Project Timeline | Discuss and adjust the project timeline | 20 | Project Team |
| Identify Potential Risks | Identify and assess potential risks | 10 | Risk Management Team |
| Discuss Budget Allocation | Review and approve budget allocation | 15 | Finance Team |
Incorporating Action Items and Decisions
Effective meetings require clear action plans and documented decisions. By explicitly incorporating action items and decision points within the meeting agenda, participants can readily understand their responsibilities and the outcomes of the meeting. This approach enhances accountability and ensures that the meeting’s objectives are achieved efficiently.The inclusion of action items and decisions within a meeting agenda, derived from the pre-meeting mind map, provides a structured framework for the meeting’s work and subsequent follow-up.
This structured approach enhances the meeting’s efficiency and ensures that agreed-upon tasks are tracked and completed.
Importance of Action Items
Action items are crucial for translating meeting discussions into concrete, actionable steps. They define who is responsible for completing specific tasks, the expected timeframe for completion, and the criteria for evaluating successful completion. Without clearly defined action items, the meeting’s objectives risk becoming mere aspirations. Action items prevent important decisions from being forgotten and provide a mechanism to track progress toward goals.
Incorporating Action Items from the Mind Map
Action items should be directly derived from the mind map’s branches, ensuring they are linked to specific topics or discussions within the meeting agenda. By tracing the connections within the mind map, relevant action items can be identified. Carefully analyze each branch to determine the required tasks and assign them to the appropriate individual.
Allocating Responsibility for Action Items
Assigning responsibility is critical for ensuring accountability and timely completion of action items. When assigning action items, consider the individual’s expertise, availability, and workload. Clearly state the specific task, expected completion date, and any required resources. A well-defined action item assignment minimizes ambiguity and promotes effective task management. This is illustrated in the example below.
- Task: Finalize the marketing strategy presentation for the Q3 launch.
- Responsible Party: Sarah Chen
- Due Date: October 26, 2024
- Status: In Progress
Template for Recording and Tracking Action Items
A structured template for recording and tracking action items is highly recommended. This template should include fields for the task description, responsible party, due date, status, and any associated documents or links. This template should be readily accessible to all participants and should be consistently used throughout the meeting process.
| Task Description | Responsible Party | Due Date | Status |
|---|---|---|---|
| Finalize presentation | Sarah Chen | October 26, 2024 | In Progress |
| Review data analysis | David Lee | October 25, 2024 | Completed |
Including Decision-Making Points
Decision points are integral to any meeting agenda. These points represent areas where consensus or agreement needs to be reached. Using the mind map as a guide, identify specific points requiring decisions. Record the decision, the rationale behind it, and the assigned responsible party for implementing the decision. This practice ensures that decisions are clearly documented and understood.
“Decisions should be recorded with the rationale and the assigned party for implementation to ensure clarity and transparency.”
Ensuring Meeting Agenda Clarity and Focus
A well-defined meeting agenda is crucial for productive outcomes. A clear and concise agenda ensures all participants understand the meeting’s purpose and objectives, fostering focused discussion and efficient use of time. This section Artikels strategies for achieving agenda clarity and focus, avoiding pitfalls, and maximizing the effectiveness of your meetings.
Strategies for Agenda Clarity
Effective agenda clarity is achieved through several key strategies. First, use precise and unambiguous language to clearly convey the purpose and desired outcomes of each agenda item. Second, prioritize agenda items logically to ensure a natural flow of discussion. Third, limit the number of agenda items to maintain focus and prevent information overload.
- Clear and Concise Language: Avoid jargon or overly complex terminology. Use simple, direct language to ensure everyone understands the agenda items. For example, instead of “strategic realignment initiatives,” use “restructuring departmental priorities.” This example illustrates the importance of avoiding ambiguous terminology, ensuring everyone understands the agenda’s objective.
- Logical Order of Items: Arrange agenda items in a logical sequence that flows naturally from one to the next. For instance, if the agenda includes discussing project updates, budget reviews, and potential risks, arrange them sequentially. This approach facilitates a smooth and focused meeting. Start with background information and progress through the more complex aspects, fostering a structured approach to the discussion.
- Concise Agenda Item Descriptions: Keep descriptions of agenda items brief and to the point. A detailed explanation is unnecessary; only the key information should be present. Provide enough context to understand the purpose of each item without overwhelming participants. Avoid unnecessary detail that could lead to confusion or distraction.
Avoiding Irrelevant Information
Inclusion of irrelevant information in the meeting agenda can lead to wasted time and reduced focus. It’s vital to ensure every item directly contributes to the meeting’s objectives. A critical step is to critically evaluate each agenda item, confirming its direct relevance to the meeting’s purpose.
- Prioritize Key Objectives: Identify the key objectives of the meeting and ensure all agenda items directly support those objectives. This focus helps avoid tangents and keeps the discussion on track.
- Review and Eliminate Irrelevant Items: Before finalizing the agenda, carefully review each item to ensure its direct relevance to the meeting’s purpose. Remove any items that are not essential to achieving the desired outcomes.
- Focus on Actionable Items: Ensure every agenda item leads to a specific action, decision, or discussion point. Avoid including items that are merely informational without a clear next step.
Logical Agenda Item Sequencing
A well-structured agenda sequence fosters a smooth and productive meeting. Presenting items in a logical order makes the meeting more efficient and reduces confusion.
- Start with Background Information: Begin with items that provide necessary background information, context, or definitions. This establishes a shared understanding for the subsequent discussion.
- Follow with Discussion Points: Follow the background information with items that require discussion or deliberation. Ensure that these items directly build on the established context.
- Conclude with Decisions and Action Items: End the agenda with items related to decisions and action items, ensuring a clear summary of the meeting’s outcomes and next steps.
Avoiding Ambiguous Language
Ambiguous language in the agenda can lead to misunderstandings and wasted time during the meeting. Clarity in language is crucial for successful meetings.
- Define Terms: If specialized terms or concepts are used, clearly define them in the agenda. Avoid assumptions about shared understanding.
- Use Specific Examples: When possible, use concrete examples to illustrate agenda items and avoid abstract or ambiguous phrasing.
- Establish a Shared Understanding: Clearly define terms and concepts to ensure all participants have a shared understanding of the agenda’s objective. This is crucial for productive discussion.
Common Agenda Pitfalls and Solutions
| Pitfall | Solution |
|---|---|
| Including too many items | Prioritize key items and limit the number of agenda points. |
| Using vague or ambiguous language | Define terms, use specific examples, and establish a shared understanding. |
| Lack of clear objectives | Define the meeting’s purpose and ensure all items contribute to achieving those objectives. |
| Including irrelevant information | Focus on items directly related to the meeting’s purpose and objectives. |
| Poorly sequenced items | Organize items logically, starting with background information, moving to discussion points, and concluding with decisions and action items. |
Visual Representation of the Agenda (Mind Map to Table)
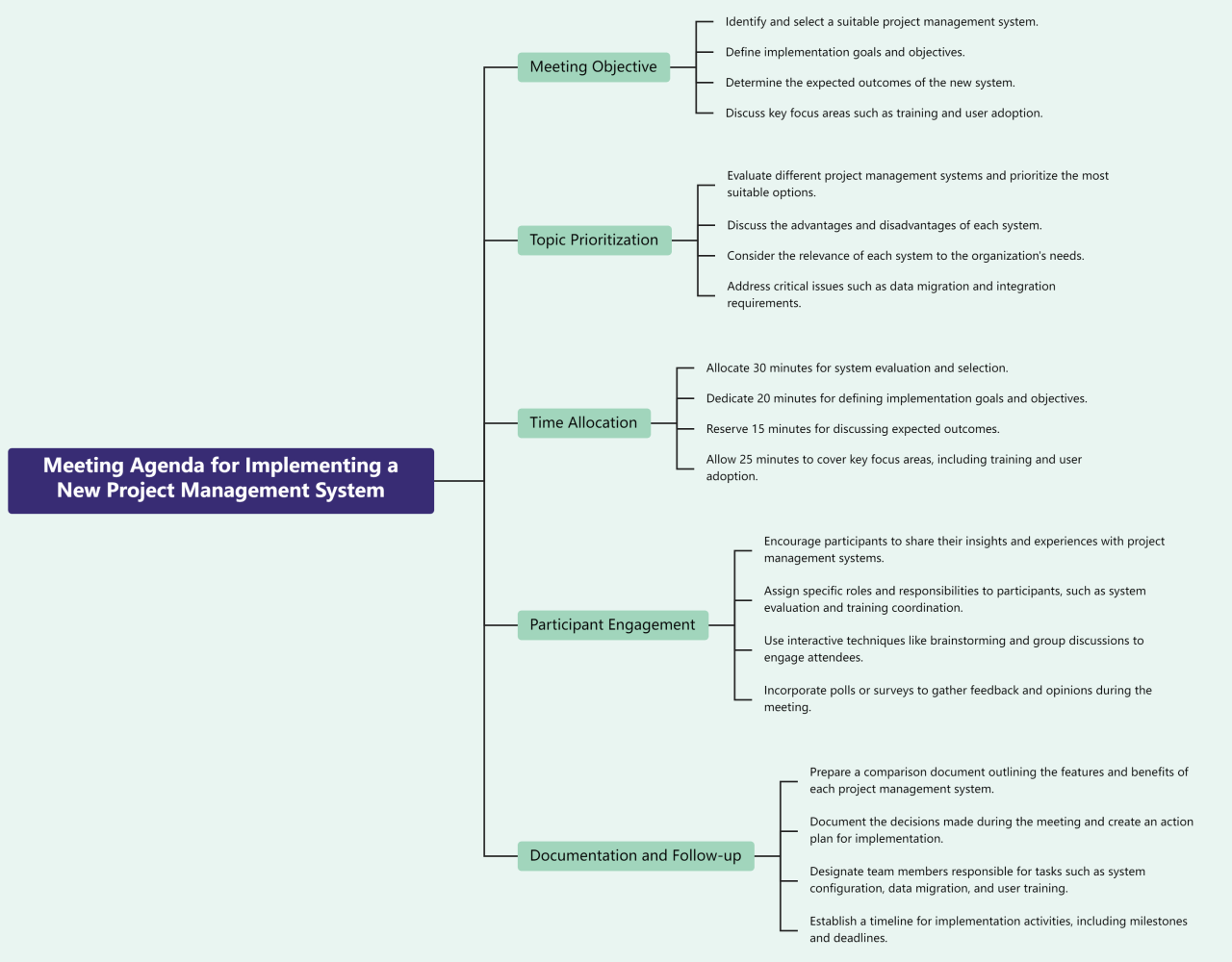
A well-structured meeting agenda, easily understood by all participants, is crucial for productive discussions. Visual representations, like mind maps, can effectively translate complex ideas into a clear and concise format. This section details the process of transforming a mind map into a structured agenda table, highlighting the importance of visual elements for enhancing clarity and engagement.
Mind Map for a Project Launch Meeting
This mind map visualizes the key components of a project launch meeting. The central theme is “Project Phoenix Launch.” Branching out from this central idea are s, each with associated points. The mind map employs color-coding and shapes to further clarify the different categories and levels of detail.
Note: A visual mind map image, if available, would be displayed here. The description below substitutes for the image. The mind map visually represents the project launch meeting agenda. The central idea is “Project Phoenix Launch”. Key branches include “Team Introductions,” “Project Overview,” “Next Steps,” and “Q&A.” Sub-branches further elaborate on these points, like “Team Roles and Responsibilities” within “Team Introductions,” and “Key Metrics” within “Project Overview.” Different colors and shapes are used to distinguish these sub-branches, improving visual clarity.
Converting the Mind Map to a Table
The following table translates the mind map into a structured meeting agenda. The table structure mirrors the hierarchical relationships in the mind map, making it easy to follow the flow of the meeting.
| Time | Topic | Description | Responsible Person |
|---|---|---|---|
| 9:00 – 9:15 | Team Introductions | Brief introductions and team roles/responsibilities | Team Leads |
| 9:15 – 9:45 | Project Overview | High-level project overview, key goals, and metrics | Project Manager |
| 9:45 – 10:00 | Next Steps | Discussion and planning of immediate actions | All Team Members |
| 10:00 – 10:15 | Q&A | Addressing questions and clarifications | Project Manager |
Visual Enhancement Techniques
Using colors and shapes in the table enhances its visual appeal and improves understanding. For example, highlighting key topics or deadlines in different colors helps to emphasize their importance. Using different shapes for different sections of the agenda can further distinguish the meeting’s flow and structure. This method improves the visual appeal of the agenda table. An example of using colors is to color-code the topics according to their categories (e.g., team introductions in light blue, project overview in orange).
Adapting the Agenda for Different Meeting Types
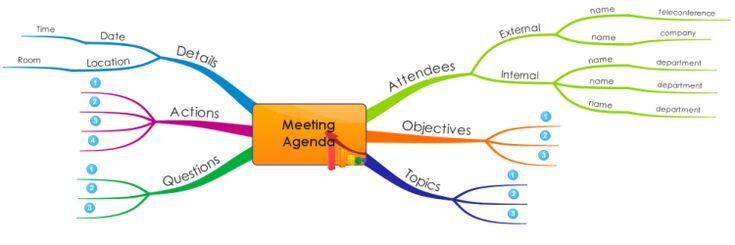
Meeting agendas are not a one-size-fits-all solution. Their effectiveness hinges on tailoring them to the specific purpose and desired outcome of each meeting. Understanding the various meeting types and their unique requirements is crucial for creating impactful and productive gatherings. This section will explore how to adapt mind map-based agenda structures to diverse meeting types.
Project Kickoff Meeting Agenda
A project kickoff meeting marks the beginning of a project. The agenda should clearly define the project scope, responsibilities, and timelines. It sets the stage for the entire project lifecycle. A well-structured kickoff meeting establishes a shared understanding of goals and expectations among all participants.
- Introduction and Welcome: Briefly introduce the project, its goals, and the participants. Review the project charter or proposal.
- Project Overview: Present the project’s scope, objectives, and deliverables. Highlight key milestones and deadlines. Explain the project’s overall vision and strategy.
- Team Introductions and Roles: Allow team members to introduce themselves and explain their specific roles and responsibilities. Clarify lines of communication and reporting structure.
- Action Items and Next Steps: Artikel the initial tasks and deadlines. Assign ownership for each task and set expectations for communication. Define the process for tracking progress.
- Q&A and Open Discussion: Facilitate a question-and-answer session to address any concerns or ambiguities. Encourage open discussion and collaboration.
Brainstorming Session Agenda
A brainstorming session is designed to generate creative ideas and solutions. The agenda should foster a relaxed and encouraging environment to maximize idea generation. Encouraging a culture of idea sharing and collaboration is key.
- Introduction and Ground Rules: Clearly define the purpose of the brainstorming session and establish ground rules for participation, such as respecting others’ ideas and avoiding criticism.
- Problem Statement/Topic Exploration: Clearly define the problem or topic to be addressed. Provide context to encourage creativity and diverse perspectives.
- Idea Generation: Allocate dedicated time for participants to contribute ideas without judgment. Use mind mapping or other visual aids to capture ideas as they emerge.
- Idea Consolidation and Categorization: Categorize and summarize the generated ideas. Use mind mapping to visualize the relationships between ideas.
- Action Items and Next Steps: Artikel next steps for developing or refining the most promising ideas.
Team Performance Review Agenda
A team performance review is a crucial opportunity to assess individual and team accomplishments. The agenda should focus on objective evaluations and identify areas for improvement. It allows for constructive feedback and goal setting.
- Review of Goals and Objectives: Review the goals and objectives established for the team at the beginning of the review period. Discuss progress toward these goals.
- Individual Performance Evaluation: Evaluate each team member’s performance based on agreed-upon metrics and criteria. Focus on quantifiable achievements.
- Feedback and Discussion: Provide constructive feedback, both positive and areas for improvement. Encourage open dialogue and two-way communication.
- Goal Setting for Next Review Period: Set SMART goals for the team and individual members for the next review period. Identify any necessary training or support.
- Action Items and Follow-Up: Artikel specific action items for addressing any identified performance gaps or areas for improvement. Assign ownership and deadlines for these items.
Adapting the Agenda
The flexibility of the mind map-based agenda is paramount. Adapting the agenda to specific meeting types and requirements is crucial. A project kickoff meeting will have a different agenda structure than a problem-solving meeting. The structure should be adaptable to various contexts.
Closing Notes
In summary, this guide provides a structured approach to creating effective meeting agendas using mind maps. By clearly defining meeting objectives, utilizing mind maps for brainstorming, and structuring the agenda with actionable items, you can significantly enhance meeting efficiency. This guide empowers you to adapt these techniques for various meeting types, ensuring a productive and focused experience for everyone involved.