Unlocking your financial potential often requires a strategic approach. This guide delves into the power of mind mapping to visualize and achieve your personal finance goals. From defining your objectives to tracking progress, we’ll explore actionable steps to transform your financial aspirations into concrete realities.
This comprehensive guide walks you through the process of crafting a personalized mind map to visualize your financial journey. We will explore different techniques for setting, prioritizing, and tracking your goals, along with actionable steps and valuable resources.
Defining Personal Finance Goals
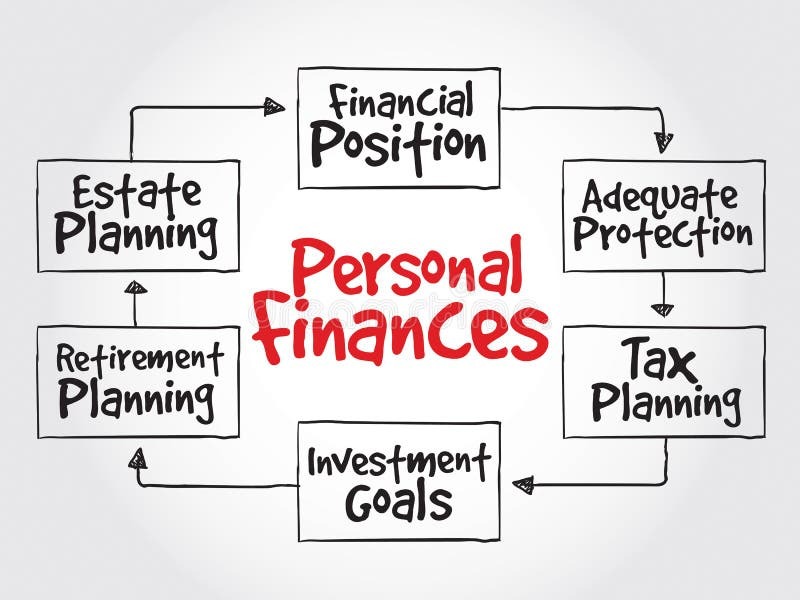
Personal finance goals are the desired outcomes individuals strive for regarding their financial well-being. These goals can range from short-term objectives to long-term aspirations, each contributing to a comprehensive financial plan. A clear understanding of these goals is crucial for making informed financial decisions and achieving lasting financial security.Clearly defined personal finance goals provide a roadmap for financial success.
They act as a guiding light, helping individuals prioritize spending, saving, and investing activities. This focused approach helps avoid impulsive decisions and promotes a structured path toward financial stability. A well-defined set of goals allows for consistent progress and helps measure success over time.
Definition of Personal Finance Goals
Personal finance goals are specific financial targets an individual sets to achieve a desired financial outcome. They encompass a range of objectives, from short-term needs to long-term aspirations. These goals are critical in guiding financial decisions and ensuring long-term financial well-being.
Importance of Clearly Defined Goals
Clearly defined personal finance goals are essential for achieving financial success. They provide a framework for making informed financial decisions and help avoid impulsive choices. This structured approach to managing finances leads to a more efficient allocation of resources and a greater chance of achieving desired outcomes. By clearly outlining financial objectives, individuals can create a roadmap for their financial future.
Examples of Personal Finance Goals
Examples of personal finance goals include saving for a down payment on a house, paying off existing debts, building an emergency fund, investing for retirement, and funding children’s education. Each goal represents a specific financial objective that requires careful planning and execution.
Steps in Identifying Personal Finance Goals
Identifying personal finance goals involves several key steps. First, evaluate your current financial situation, including income, expenses, and debts. Next, consider your short-term and long-term aspirations. This includes considering your lifestyle goals, family needs, and future aspirations. Finally, prioritize these goals based on their urgency and importance.
The process is ongoing and requires regular review and adjustments as circumstances evolve.
Types of Personal Finance Goals
This table Artikels various types of personal finance goals, their descriptions, and associated timeframes.
| Goal Type | Description | Timeframe |
|---|---|---|
| Emergency Fund | Accumulating funds to cover unexpected expenses, such as job loss, medical emergencies, or car repairs. | Short-term (3-6 months of living expenses) |
| Debt Repayment | Reducing or eliminating outstanding debts, such as credit card balances, student loans, or mortgages. | Short-term to medium-term (ranging from months to years) |
| Home Purchase | Saving for a down payment and closing costs associated with buying a home. | Medium-term to long-term (2-5 years) |
| Retirement Savings | Accumulating funds for retirement expenses, including living costs, healthcare, and leisure activities. | Long-term (20-30+ years) |
| Education Funding | Saving for children’s or family members’ educational expenses, including tuition, fees, and living costs. | Medium-term to long-term (5-18 years) |
Visualizing Goals with Mind Maps
Mind maps provide a powerful visual tool for organizing and connecting personal finance goals. They transform abstract financial objectives into a readily understandable, interconnected structure, fostering a clearer perspective on the path to achieving your aspirations. This visual representation helps identify dependencies and potential roadblocks, making your financial plan more dynamic and responsive to evolving circumstances.By visually representing your financial aspirations, mind maps enhance understanding and engagement, making the process of achieving financial goals more manageable and motivating.
This visual representation promotes a holistic approach to personal finance, encouraging a deeper comprehension of the interrelationships between different financial objectives.
Creating a Mind Map for Buying a House
A mind map for purchasing a house can effectively illustrate the interconnected steps involved. The central theme, “Buy a House,” can branch out into key areas like saving for a down payment, securing a mortgage, and managing the associated costs. Each of these branches can further be broken down into sub-branches, such as budgeting, finding a suitable home, and navigating the mortgage process.
This detailed structure makes it easier to see how each element contributes to the overall goal.
- Saving for a Down Payment: This branch will include specific savings targets, timelines, and potential income streams to achieve the desired amount. A detailed breakdown of monthly savings contributions, emergency fund contributions, and potential investments to grow the down payment fund is crucial.
- Securing a Mortgage: This section details the steps needed to qualify for a mortgage, including credit score improvement strategies, debt management plans, and the required documentation. It should also incorporate research on different mortgage types, interest rates, and loan terms.
- Managing Associated Costs: This branch will cover closing costs, moving expenses, property taxes, homeowner’s insurance, and potential repairs. A budget allocation for each expense should be included.
- Finding a Suitable Home: This includes research on the desired location, budget, and property features. It also encompasses the process of house hunting, comparing properties, and making an offer.
Constructing a Mind Map for Financial Freedom
A mind map for achieving financial freedom is a comprehensive visual representation of your financial aspirations, detailing the key areas and their interdependencies. The central theme, “Financial Freedom,” should branch out into crucial components such as building wealth, minimizing expenses, and securing a sustainable income.
- Building Wealth: This branch encompasses strategies for investment, including stocks, bonds, real estate, and other assets. It also details a timeline for achieving wealth accumulation goals and the required risk tolerance.
- Minimizing Expenses: This branch should detail strategies for reducing living expenses, including identifying areas for cost reduction, such as utilities, subscriptions, and transportation.
- Securing a Sustainable Income: This branch includes strategies for increasing income, exploring potential career advancements, or diversifying income streams. It also includes plans for financial security, such as investing in passive income sources.
Benefits of Using Mind Maps for Personal Finance Planning
Mind maps offer several advantages in personal finance planning. They facilitate a holistic approach to financial management, enabling individuals to visualize the interconnectedness of various financial objectives. This visual representation enhances understanding, fostering a deeper comprehension of the interrelationships between different financial objectives. Furthermore, mind maps promote a dynamic approach to planning, allowing for adjustments based on changing circumstances.
Retirement Planning Mind Map Example
This example focuses on a hypothetical individual planning for retirement. The central theme is “Retirement Planning.” Key branches include Income, Expenses, and Savings.
| Category | Details |
|---|---|
| Income | Current salary, potential future salary increases, investment income, social security benefits. |
| Expenses | Housing, utilities, food, transportation, healthcare, entertainment. Detailed projections of expenses throughout retirement. |
| Savings | Current savings, required savings to achieve retirement goals, investment strategies, and potential for growth. |
This example demonstrates how a mind map can visually represent the crucial elements of retirement planning.
Strategies for Goal Setting and Prioritization

Effective personal finance management hinges on well-defined goals and strategic prioritization. A clear roadmap, encompassing both short-term and long-term objectives, empowers individuals to make informed financial decisions. This section delves into various methods for setting goals, the crucial SMART framework, and techniques for prioritizing them, ultimately equipping you with a robust plan for achieving your financial aspirations.Setting financial goals is a multifaceted process, requiring a deep understanding of individual needs and aspirations.
A well-structured approach can transform vague desires into concrete, actionable plans, ensuring your financial journey remains focused and productive.
Methods for Setting Personal Finance Goals
Setting personal finance goals involves a process of reflection and planning. Different methods cater to varying preferences and needs. Some popular methods include:
- Vision Boards: Creating visual representations of financial goals can be a powerful motivator. A vision board visually represents desired outcomes, making them more tangible and reinforcing commitment. Visualizing goals can make them more engaging and memorable, fostering a stronger sense of purpose.
- Financial Planning Software: Utilizing dedicated software can provide structure and support for goal setting. Many platforms offer templates, tools, and trackers to help individuals document their progress towards financial goals.
- Goal Journals: Maintaining a dedicated journal to document financial goals can serve as a powerful tool. This allows for detailed recording of goals, progress, and adjustments needed throughout the journey.
The SMART Goals Framework for Personal Finance
The SMART framework, a cornerstone of effective goal setting, ensures that financial objectives are well-defined and achievable. It provides a structured approach to goal creation and management.
SMART goals are Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, and Time-bound.
This framework is particularly useful for personal finance goals as it translates broad aspirations into actionable steps.
Specific
Clearly defining the goal is crucial. Instead of “save more,” a SMART goal would be “save $5,000 for a down payment on a house within the next three years.”
Measurable
Quantifying the goal enables progress tracking. For example, instead of “improve credit score,” a SMART goal would be “increase credit score from 650 to 700 by the end of the year.”
Achievable
Goals must be realistic and attainable within the available resources and time frame. Setting an unrealistic goal can lead to discouragement and abandonment.
Relevant
The goal must align with overall financial objectives and life aspirations. For instance, saving for a down payment on a house is relevant if homeownership is a primary financial goal.
Time-bound
Establishing a deadline adds urgency and structure. A SMART goal would include a specific date or timeframe for achieving the goal.
Prioritization Techniques for Personal Finance Goals
Prioritization techniques assist in managing multiple goals effectively. They help determine which goals to address first based on their impact and urgency.
- Pareto Principle (80/20 Rule): Focus on the 20% of your goals that will yield 80% of the results. Identifying and prioritizing these high-impact goals can significantly accelerate progress.
- Eisenhower Matrix: This matrix categorizes tasks based on urgency and importance. Prioritizing urgent and important tasks first ensures critical needs are addressed effectively.
Prioritizing Goals Based on Impact and Urgency
Prioritizing goals based on their impact and urgency ensures effective resource allocation. High-impact, high-urgency goals should be addressed first.
| Category | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| High Impact, High Urgency | Goals with significant impact and immediate deadlines. | Paying off high-interest debt. |
| High Impact, Low Urgency | Goals with significant impact but flexible deadlines. | Investing for retirement. |
| Low Impact, High Urgency | Goals with minimal impact but immediate deadlines. | Paying a small utility bill. |
| Low Impact, Low Urgency | Goals with minimal impact and flexible deadlines. | Buying a new gadget. |
Steps for Using the SMART Framework in Setting Personal Finance Goals
- Define your goal: Clearly articulate the desired outcome, such as “save $10,000 for a down payment on a new car.”
- Make it measurable: Quantify the goal, such as “save $10,000 by the end of the year.”
- Ensure it’s achievable: Evaluate the resources available and determine if the goal is realistic.
- Assess relevance: Determine if the goal aligns with your overall financial objectives.
- Set a time frame: Establish a deadline for achieving the goal, such as “save $10,000 by December 31, 2024.”
Incorporating Resources and Tools
Successfully managing personal finances often requires leveraging various resources and tools. This section will explore the diverse range of available support, from budgeting apps to financial advisors, empowering you to achieve your financial goals more effectively. We’ll also examine reputable online tools and resources, providing a comprehensive guide to optimizing your financial planning process.Effective personal finance management relies heavily on the appropriate use of available resources.
This involves understanding the strengths and weaknesses of different tools and methods to create a personalized strategy. By thoughtfully incorporating these resources, you can streamline your financial planning, track progress, and make informed decisions.
Different Resources for Personal Finance Planning
A wide array of resources are available to support your personal finance journey. These range from readily accessible online calculators and budgeting apps to the expert guidance of financial advisors. Understanding the options and their specific strengths will allow you to select the most suitable tools for your needs.
- Budgeting Apps: These apps provide a digital platform for tracking income and expenses, setting budgets, and generating financial reports. They often offer features like automated categorization of transactions, goal setting, and notifications for exceeding budget limits. This simplifies the budgeting process and provides clear insights into spending habits. For example, Mint or Personal Capital can track your accounts, and many offer features to help with saving and investing.
- Financial Advisors: Certified financial planners can offer personalized guidance and support for various financial goals. They can assist with investment strategies, retirement planning, and debt management. Their expertise can help you navigate complex financial situations and make informed decisions, potentially leading to greater returns and improved financial well-being. For instance, a financial advisor can help determine the best investment options for retirement or create a comprehensive plan to pay off high-interest debt.
- Online Calculators: Numerous online calculators provide quick estimates for various financial situations. These tools can be used to calculate loan payments, estimate retirement savings needs, or determine the cost of education. They offer convenient ways to gain insights into potential financial outcomes without requiring extensive knowledge of financial formulas. For example, a mortgage calculator can quickly show you the monthly payments for different loan amounts and interest rates.
Reputable Online Tools and Resources
Numerous websites and online platforms offer valuable information and tools to support personal finance. These resources often include articles, calculators, and guides, empowering users with knowledge and practical tools. Reliable sources are essential for informed financial decisions.
- NerdWallet: Provides a wealth of information on personal finance topics, including budgeting, saving, investing, and debt management. They offer practical tips and tools to help users navigate their financial journey. NerdWallet is known for its unbiased, comprehensive guides and comparisons of financial products.
- Investopedia: Offers a vast library of financial articles and definitions. This resource is particularly useful for understanding complex financial concepts and terms. Investopedia helps users build a strong foundation of knowledge in the financial world.
- The Motley Fool: A popular financial website and blog, known for its investment analysis and insights. The Motley Fool provides actionable strategies for building wealth through investing. It offers a comprehensive approach to personal finance, especially for those looking to make long-term investment plans.
Financial Planning Software Features and Benefits
Financial planning software packages offer a more comprehensive approach to managing personal finances. These programs combine various tools and features to streamline the process. The benefits can be significant, allowing users to create detailed financial plans and track progress.
- Comprehensive Financial Planning Software: These programs provide a centralized platform to manage budgets, track investments, monitor retirement savings, and manage debts. They often offer advanced features such as personalized financial reports and projections. These platforms often provide greater clarity into financial well-being, offering insight into various financial aspects of life.
- Advanced Features: Many software packages incorporate tools for investment tracking, portfolio management, and tax planning. These advanced features help users optimize their financial strategies and make informed decisions. These functionalities can significantly impact the long-term financial health of individuals.
Comparison of Budgeting Methods
Different budgeting methods cater to various needs and preferences. Understanding the characteristics of each method can help you select the best approach for your circumstances.
| Budgeting Method | Description | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|---|
| Zero-Based Budgeting | Allocates every dollar of income to a specific category. | Forces careful spending and awareness of every financial transaction. | Can be overly complex and time-consuming for some individuals. |
| 50/30/20 Budgeting | Divides spending into needs (50%), wants (30%), and savings/debt repayment (20%). | Simple and easy to understand, promotes a balanced approach to spending. | May not be suitable for those with complex financial situations or high debt levels. |
| Envelope Budgeting | Assigns cash to specific categories in envelopes. | Encourages physical awareness of spending. | Less flexible and less suitable for digital transactions. |
Tracking Progress and Adapting Strategies
Monitoring your personal finance goals is crucial for staying on track and achieving your desired outcomes. Regular progress tracking allows you to identify areas where you are excelling and areas needing adjustments. This proactive approach empowers you to adapt your strategies in response to evolving circumstances and unexpected events, ultimately increasing your chances of success.Effective monitoring involves a blend of meticulous record-keeping and strategic analysis.
By consistently documenting your financial activities and evaluating their impact on your goals, you can make informed decisions and fine-tune your strategies to maintain a positive trajectory. This proactive approach to tracking and adapting is vital for weathering unexpected financial storms and capitalizing on opportunities.
Methods for Monitoring Progress
Tracking progress towards your personal finance goals requires a structured approach. Regular review of your financial data is key. This involves analyzing your income, expenses, savings, and investments to assess how they align with your planned path. Regular evaluations allow you to pinpoint areas where adjustments are needed.
Tracking Expenses, Savings, and Investments
To effectively monitor expenses, savings, and investments, utilize a combination of digital tools and manual record-keeping. Spreadsheet programs, budgeting apps, or personal finance management software are excellent for organizing and analyzing financial data. Manually recording transactions ensures a comprehensive overview of your financial situation.
- Expense Tracking: Categorize expenses to understand where your money is going. This allows you to identify areas where you can cut back or redirect funds towards your goals. For example, a detailed breakdown of expenses (e.g., groceries, entertainment, transportation) reveals patterns and potential areas for optimization.
- Savings Tracking: Monitor your savings progress by tracking deposits and withdrawals. This gives you a clear picture of your savings growth and allows you to compare it to your projected savings goals.
- Investment Tracking: Maintain records of your investments, including the date of purchase, quantity, price, and any associated fees. Analyzing investment performance against projected returns helps you assess the effectiveness of your investment strategy.
Adjusting Strategies Based on Changing Circumstances
Life is dynamic, and financial circumstances inevitably change. Adapting your strategies to these shifts is crucial for maintaining momentum toward your goals. Economic downturns, job changes, or unexpected medical expenses can all impact your financial plans. Flexibility and proactive adjustments are vital.
- Economic Downturns: During economic downturns, consider adjusting your investment portfolio to mitigate potential losses. Diversification and careful risk management are crucial. For instance, during a recession, you might shift a portion of your portfolio from high-growth stocks to more stable bonds.
- Job Changes: A job change can alter your income and expenses. Reassess your budget and adjust your savings and investment strategies to reflect your new financial situation. For example, a promotion with a higher salary might allow you to increase your savings rate or invest more aggressively.
- Unexpected Expenses: Life often throws unexpected events like medical emergencies or home repairs. Having an emergency fund can help you weather these storms without jeopardizing your long-term financial goals. Ensure your emergency fund is adequate to cover unforeseen expenses.
Adapting to Unexpected Events and Financial Challenges
Life throws unexpected curves. A crucial aspect of effective personal finance management is adapting to these unpredictable events. Having a plan for setbacks is essential. This involves incorporating potential obstacles into your mind map and developing contingency plans.
- Financial Setbacks: Unforeseen financial setbacks, such as job loss or unexpected medical bills, can derail your progress. Having a robust emergency fund can cushion the blow and allow you to maintain your financial stability.
- Mind Map Adjustments: Incorporating setbacks into your mind map helps you visualize how these events might affect your goals and enables you to adapt your strategies accordingly. For instance, a temporary loss of income might necessitate a reduction in discretionary spending and a focus on increasing emergency savings.
Incorporating Setbacks into Your Mind Map and Adjusting Strategies
A well-designed mind map can visually represent potential setbacks and strategies for overcoming them. This visualization allows for a clear understanding of the impact of these events and provides a roadmap for adjustments.
- Identifying Potential Setbacks: Consider potential financial challenges, both foreseeable and unforeseen, and document them on your mind map. This process includes evaluating risks and developing contingency plans.
- Adapting Strategies: If a setback occurs, use your mind map as a guide to adjust your strategies. This might involve reducing spending, increasing savings, or shifting investment allocations.
Maintaining Motivation and Consistency

Sustaining motivation is crucial for achieving personal finance goals. It’s not enough to define goals; the commitment and consistent effort required to reach them are equally vital. Maintaining momentum throughout the process, even when faced with setbacks, is paramount to success. This section explores strategies for overcoming obstacles, staying focused, and recognizing common challenges, ultimately empowering you to maintain consistency in your financial journey.Achieving financial goals often requires sustained effort and resilience.
The path to financial well-being is rarely a straight line; unexpected events, personal setbacks, or shifts in priorities can impact progress. Understanding these potential roadblocks and developing strategies to navigate them proactively is essential for staying on track and maintaining motivation. Developing a proactive mindset, coupled with effective techniques, is key to long-term success.
Importance of Maintaining Motivation
Maintaining motivation is essential for consistently pursuing and achieving personal finance goals. A strong sense of purpose and motivation fuels the drive needed to overcome challenges, stay disciplined, and make necessary sacrifices. Without it, the initial enthusiasm often wanes, leading to procrastination and ultimately, abandonment of goals. This can result in missed opportunities for financial growth and stability.
Strategies for Overcoming Obstacles and Maintaining Consistency
Maintaining consistency in pursuing financial goals necessitates a proactive approach to obstacle management. Regular self-reflection, adjusting strategies as needed, and seeking support from trusted individuals can significantly contribute to sustained effort. These strategies form the foundation for maintaining consistency and momentum in achieving financial aspirations.
- Regular Review and Adjustment: Periodically evaluating your progress, identifying roadblocks, and adjusting your strategies is vital. This proactive approach allows you to adapt to changing circumstances and maintain momentum. For instance, if a planned investment isn’t performing as expected, a review can lead to a change in investment strategy.
- Breaking Down Large Goals: Large, overarching financial goals can feel daunting. Breaking them down into smaller, more manageable steps can make them less overwhelming and more attainable. This approach allows for a sense of accomplishment with each milestone reached, fostering motivation and consistency. For example, saving for a down payment on a house can be broken down into monthly savings targets.
- Seeking Support and Accountability: Sharing your goals with trusted friends, family, or a financial advisor can provide encouragement and accountability. Knowing you’re not alone in your journey can significantly boost motivation and encourage consistent effort. A support network can provide guidance and encouragement during challenging times.
Techniques for Staying Focused and Inspired
Staying focused and inspired in pursuing financial goals requires consistent self-care and a proactive approach. This includes prioritizing tasks, establishing realistic timelines, and celebrating milestones. Techniques for self-motivation and continuous inspiration are key for long-term success.
- Prioritizing Tasks: Establishing a clear hierarchy of financial tasks helps to focus efforts on the most important and urgent aspects of your financial plan. This prioritization allows for a more efficient use of time and energy, which can significantly impact motivation and consistency.
- Setting Realistic Timelines: Unrealistic timelines can lead to frustration and demotivation. Setting achievable and realistic timelines for reaching milestones fosters a sense of accomplishment and maintains motivation. This approach encourages consistent effort and prevents burnout.
- Celebrating Milestones: Acknowledging and celebrating progress, no matter how small, reinforces positive behavior and maintains motivation. This recognition of accomplishments motivates continued effort and fosters a sense of progress towards financial goals.
Common Challenges Faced When Trying to Achieve Financial Goals
Several factors can hinder the pursuit of financial goals. These challenges, if not addressed proactively, can lead to demotivation and abandonment of the desired outcome. Understanding and acknowledging these challenges is the first step in overcoming them.
- Lack of Financial Literacy: A lack of understanding about personal finance concepts can make it difficult to develop and execute a sound financial plan. This lack of knowledge can hinder progress and demotivate individuals.
- Financial Instability: Unexpected life events, job loss, or economic downturns can disrupt financial plans and lead to demotivation. Adapting to these challenges requires resilience and a proactive approach.
- Procrastination and Impulsiveness: Procrastination and impulsive spending habits can significantly hinder progress towards financial goals. Developing discipline and delaying gratification are crucial for long-term financial success.
Motivational Techniques for Personal Finance
Different motivational techniques can be employed to support and sustain the pursuit of personal finance goals. A combination of approaches tailored to individual needs and preferences can be most effective.
| Technique | Description | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|---|
| Visual Goal Setting | Creating visual representations of financial goals, such as a vision board. | Increases awareness and motivation. | Requires creativity and may not be effective for everyone. |
| Reward Systems | Establishing rewards for achieving milestones. | Reinforces positive behavior and increases motivation. | May become unsustainable if rewards are not well-defined or are too frequent. |
| Accountability Partners | Collaborating with a friend or family member to track progress. | Provides support and encouragement. | Requires trust and commitment from the partner. |
| Mindfulness and Meditation | Practicing mindfulness to manage stress and focus on goals. | Improves mental clarity and reduces anxiety. | Requires discipline and may not be suitable for all individuals. |
Wrap-Up

In conclusion, using mind maps for personal finance allows you to organize your goals, track progress, and adapt to life’s unexpected twists. By combining visualization with strategic planning, you can achieve financial freedom more effectively. This guide provides a roadmap for success, empowering you to navigate your financial future with clarity and confidence.